How can you tell if your kidney stone is about to pass? Learn to see the signs that can bring some predictability to an otherwise painful process.
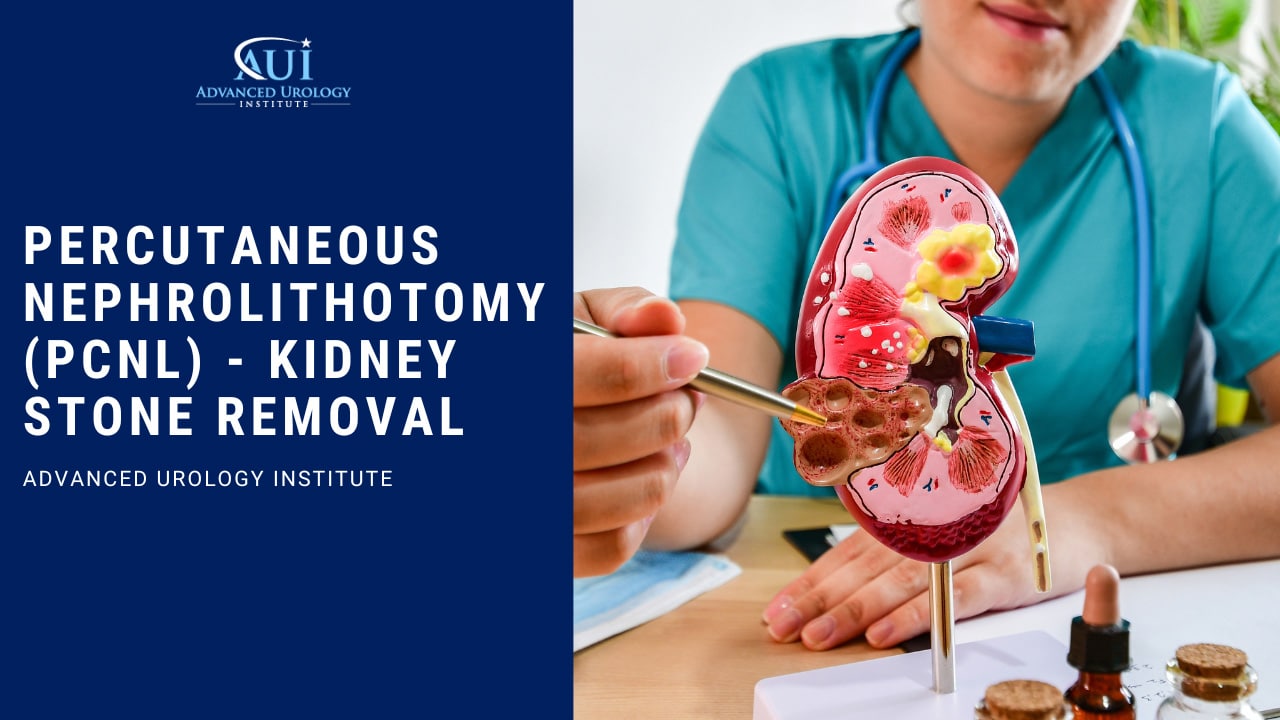
Continue readingPercutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) – Kidney Stone Removal
Advancements in urology now lead to better treatment solutions for kidney stones such as precutaneous nephrolithotomy or PCNL.
Continue readingChristopher Sherman, MD: A Comprehensive Overview of Kidney Stones and Treatment Options
Exploring the World of Kidney Health🩺📚 Christopher Sherman, MD: A Comprehensive Overview of Kidney Stones and Treatment Options
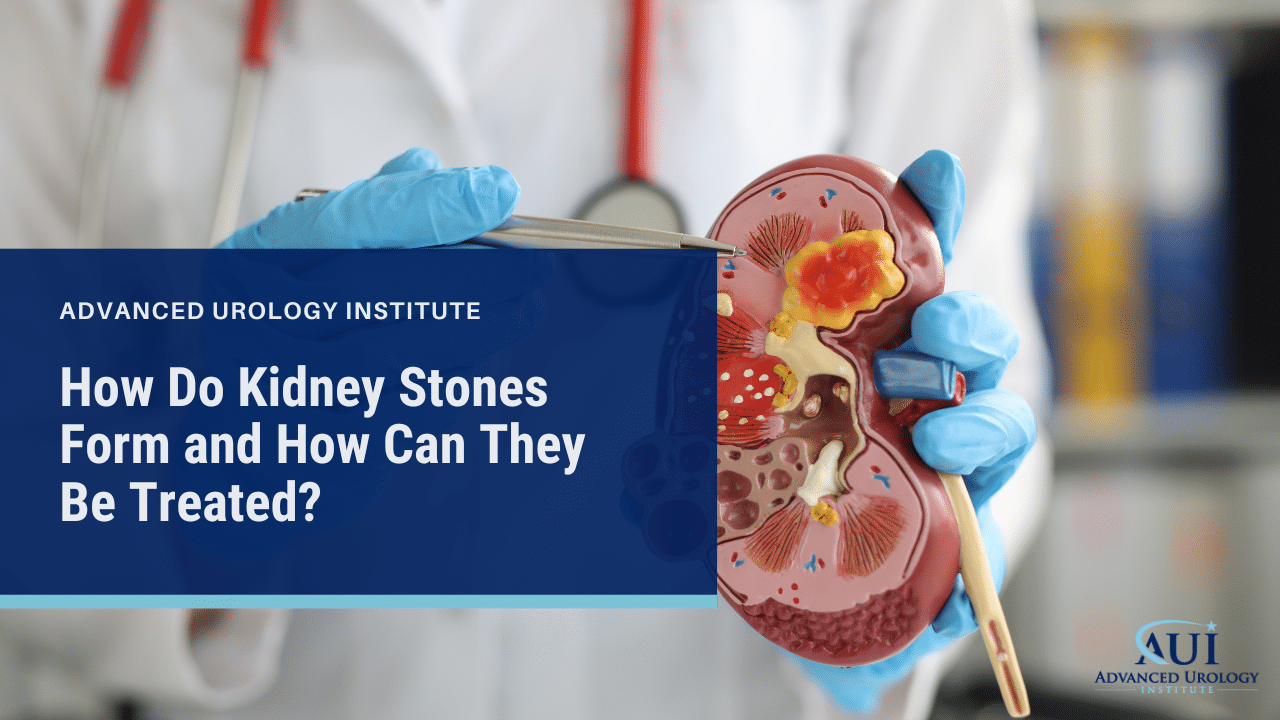
Continue readingHow Do Kidney Stones Form and How Can They Be Treated?
Unlocking the Mystery and Solutions! How Do Kidney Stones Form and How Can They Be Treated? Learn more at Advanced Urology Institute now.
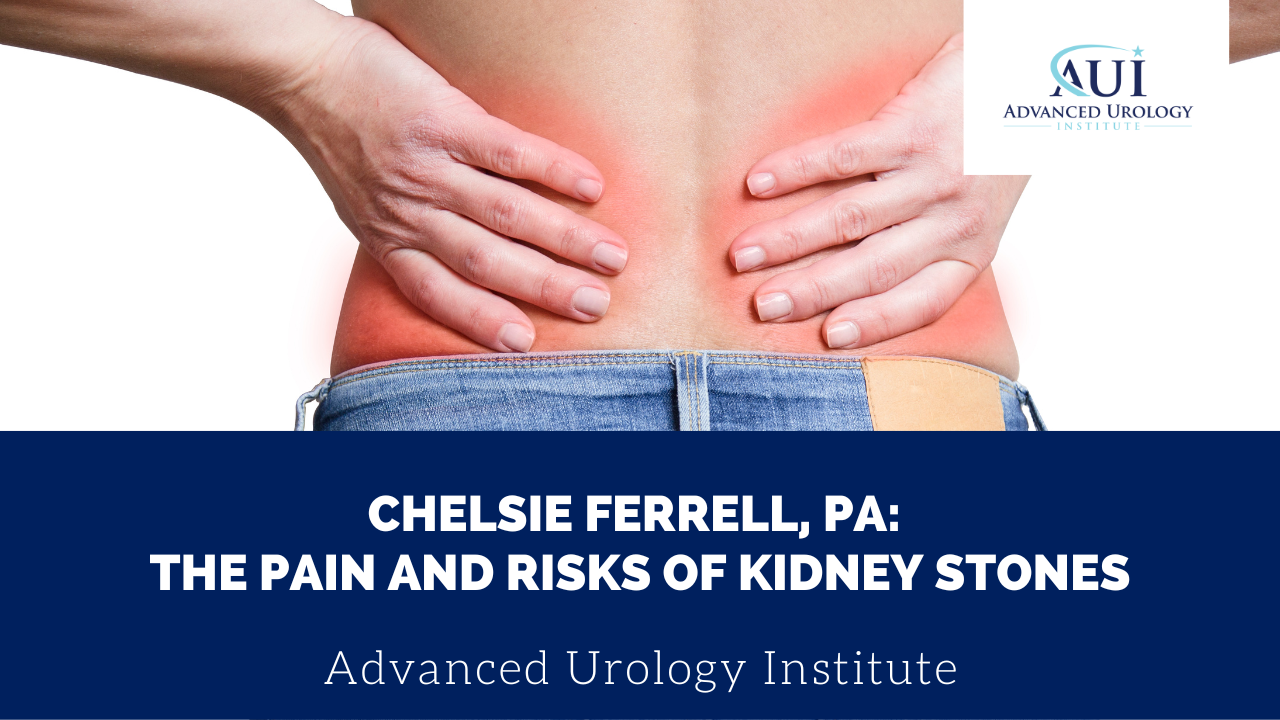
Continue readingChelsie Ferrell, PA: The Pain and Risks of Kidney Stones
Expert Insights: Chelsie Ferrell, PA, on the Pain and Risks of Kidney Stones. Learn How to Prevent & Treat this Common Condition. Read More!
Continue readingHow Has Advanced Urology Institute Revolutionized Urological Care?
Transforming Urological Care: Discover How Advanced Urology Institute Leads the Revolution! Innovations & Patient-Centered Excellence
Continue readingIs Your Kidney Health at Risk this 4th of July?
Can kidney stones go away on their own?
7 Signs You Might Have Kidney Stones
Can Dr. Samuel Lawindy provide treatment for large kidney stones?
How Do You Treat Kidney Stones
Treating kidney Stones depends on the degree of the pain the size of stone. Learn more from Dr. Billy Vanasupa of St Augustine, FL.
Continue readingWhat are the treatment options for kidney stones?
Not many medical problems are as frustrating and as unbearably painful as kidney stones. With urinary stones, you experience a severe, sharp pain in your side and back. The pain comes in waves, fluctuates in intensity, and radiates to the lower abdomen and groin.
Continue readingWhat are the Conditions We Treat at Advanced Urology Institute?
Kidney Stones Symptoms with Dr. Brian Hale
So patients who have kidney stones usually complain of flank pain, which is where the pain would be behind the lower ribs and sometimes it wraps around towards the front [and] down towards the groin area. Those are the most common symptoms, [sometimes] they’ll also have blood in the urine on our testing in the office.
Usually we’ll get an ultrasound or CT scan that diagnoses the stone, it’ll tell us the size and location. If the stones are smaller [about] less than 4 millimeters in size, ninety (90) percent of those times it will pass on their own. So on those patients, I give them a chance to try to pass the stone before we operate on them. When they’re bigger, they’ll be more than 6 millimeters in size, the less of a change of passing [the stone], less than ten (10) percent. For those patients, we look at the scheduling surgery for.
Kidney Stones: Risk Factors and Preventions
 The prevalence of kidney stones in the United States has increased over the last decade. As many as 1 in 10 Americans have a kidney stone at some point in their lives, and every year more than half a million Americans go to emergency rooms for kidney stone related complications.
The prevalence of kidney stones in the United States has increased over the last decade. As many as 1 in 10 Americans have a kidney stone at some point in their lives, and every year more than half a million Americans go to emergency rooms for kidney stone related complications.
What are kidney stones?
A kidney stone is a small, hard deposit that forms in the kidneys. Stones occur when the urine concentration of crystal-forming substances—such as calcium, oxalate and uric acid—is more than the fluid in the urine can dilute.
They begin as small crystals and grow into larger masses (stones), which then make their way through the urinary tract. Unfortunately, a stone can get stuck on its way out of the urinary system, resulting in an unbearable pain that comes in waves until the stone eventually passes.
What causes kidney stones?
Genetics is one of the risk factors. If you have family members who had kidney stones, you are at a higher risk of having them yourself. Your risk is also higher if you have had kidney stones in the past.
Dehydration is another major cause of kidney stones, which is why more kidney stones occur in the summer. In fact, kidney stone frequency is known to vary by geographic location, with warmer climates having the highest rates of stone formation.
What you eat and drink makes a huge difference. Drinking enough fluids to make over two liters of urine a day reduces the risk of stone formation. Actually, as a rule, you should always check your urine for signs of dehydration. If your urine is dark or yellow, then you are not drinking enough fluid and run the risk of having stones.
Factors that increase dehydration will contribute to kidney stone formation. For instance, excess salt or sodium in food, such as in processed or fast foods, increase dehydration as the excess salt requires a lot of fluid to excrete. So reducing the sodium in your diet will minimize your risk of stone formation.

How do you know that you have kidney stones?
Kidney stones cause pain by getting stuck in the urinary system. Since the kidneys continue to make urine, which in turn can’t get out due to the blockage, the urine builds up, stretches the kidneys and leads to severe pain.
You will know you have kidney stones when you have severe, excruciating pain that comes in waves. The pain typically occurs in the back and does not get better with a change in position. Patients who have had kidney stones and also delivered children report that the stones are more painful than giving birth. In addition to pain, you may have fever, nausea, and even vomiting.
Kidney stones may require a trip to the emergency room if you have severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and a fever greater than 100.3 degrees. These symptoms constitute a urological emergency because they signal both a blockage and an infection. With the blockage preventing antibiotics from getting out via urine, you can get very sick, very quickly; hence the need for emergency care.
Emergency treatment with IV fluids at a hospital may be necessary if you are having nausea and vomiting to the point of dehydration. Emergency care is also appropriate when you have pain that cannot be alleviated by over-the-counter pain medicine.
What is the treatment for kidney stones?
The treatment for kidney stones depends on the size and location of the stone, and on the clinical stability of the patient. The most common approach is medical expulsion therapy—a conservative approach for healthy patients with stones that are small enough to pass on their own and with no fever or other signs of infection.
With medical expulsion, you are encouraged to drink a lot of fluid to help the stone pass on its own. You are also given medications to control the pain and to accelerate passage. If the stone is 5 millimeters or smaller (about half of your thumbnail), there is a 50% chance it will pass on its own and you will avoid surgery.
If you have severe pain, fever, chills and an inability to drink fluids, you may not qualify for medical expulsion therapy. In that case, a surgical procedure may be needed. There are two common surgical options: (1) ureteroscopy or laser lithotripsy, and (2) extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy.
Ureteroscopy and laser lithotripsy are fancy ways of saying you go to sleep, a camera is inserted through your urethra to the stone, and a laser is used to break the stone into smaller fragments for removal. Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy means you go to sleep and sound waves are sent through your skin to fracture the stone into small pieces that can pass on their own in urine.
The advantage of shockwave lithotripsy is that nothing goes into your body, making it less invasive. However, the disadvantage is that the stone fragments still have to pass on their own, a process which can be painful and uncomfortable.
How do you prevent kidney stones?
1. Increase calcium intake
There is a misconception that increasing dietary calcium increases the risk of calcium oxalate stones. This is not true. In fact, eating more calcium rich foods, such as milk or cheese, ensures the oxalate in the diet binds to calcium. When oxalate binds to calcium in the intestines, it is not absorbed in the bloodstream and ends up in stool.
2. Reduce oxalate rich foods
Foods high in oxalate, such as beets, chocolate, tea, coffee, spinach, kale, rhubarb, nuts and beer contribute to stone formation. You may have to eat smaller portions of these foods alongside calcium-rich foods or avoid them altogether.
3. Stay hydrated
Drinking plenty of water will ensure that substances in your urine are diluted and cannot form crystals. As a rule, strive to drink enough water to pass two liters of urine every day—which is drinking roughly eight standard 8-ounce cups per day. It also helps to include some citrus beverages, such as orange juice and lemonade, as the citrate in these beverages helps to block stone formation.
4. Reduce sodium intake
A high salt or sodium diet increases the amount of calcium in your urine and triggers stone formation. Excess salt also wastes the fluid you take as a lot more fluid is necessary for salt-water balance. Make sure to limit your daily sodium intake to 2300mg or less to reduce your risk of kidney stones.
5. Minimize intake of animal protein
Animal protein, such as red meat, eggs, poultry, or seafood, increases the level of uric acid in the body and may cause kidney stones. A high protein diet will also reduce your urinary citrate—the chemical in urine that prevents stones from forming. You can limit animal proteins or replace them with plant-based proteins.
At Advanced Urology Institute, we offer a range of treatments for kidney stones depending on the severity of symptoms and the type, size and location of the stones. We also run tests to find out why they form and give you advice on how to prevent them.
If you or a relative has had kidney stones, consider meeting with one of our urologists for specific ways to reduce your risk. For more information on kidney stone causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment and prevention, visit the Advanced Urology Institute website.
Listen to the Podcast to learn more about Kidney Stones, Click here




 As the 4th of July approaches, you might be planning a grand celebration with fireworks, barbecues, and a few rounds of beer. But amidst the excitement of Independence Day, have you considered the potential risk to your kidney health?
As the 4th of July approaches, you might be planning a grand celebration with fireworks, barbecues, and a few rounds of beer. But amidst the excitement of Independence Day, have you considered the potential risk to your kidney health?